
Location and Boundaries
Island and tropical, with the Atlantic and the Caribbean coiled around its coasts the Dominican Republic occupies two thirds of the island that it shares with Haiti in the Antilles archipelago. Situated between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea , it is part of the Tropic of Cancer, in the Northern Hemisphere, and it can be found exactly between 68°19” and 72°31’ west longitude and 17º30′ and 19º56′ north latitude, which determines its tropical climate.
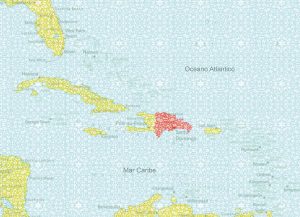 With a privileged position in the Caribbean, between the islands of Cuba and Puerto Rico, it shares the island of Hispaniola with the Republic of Haiti . The Atlantic Ocean bathes its northern coast and the Caribbean seaboard is to the east and south, while the Republic of Haiti extends to the west, with an area of 27,700 square kilometers.
With a privileged position in the Caribbean, between the islands of Cuba and Puerto Rico, it shares the island of Hispaniola with the Republic of Haiti . The Atlantic Ocean bathes its northern coast and the Caribbean seaboard is to the east and south, while the Republic of Haiti extends to the west, with an area of 27,700 square kilometers.
Due to its 48,198 square kilometer area, including adjacent islands, the Dominican Republic is second place in size among the countries of the Major Antilles. It is approximately 837 nautical miles from Florida, United States and approximately 70 nautical miles from Puerto Rico.
Geographic boundaries
- To the north:Atlantic Ocean.
- To the south:Caribbean Sea or Antillean Sea.
- To the east:La Mona Passage.
- To the west:Republic of Haiti.
Maritime Boundaries
Territorial sea: 6 nautical miles.
Exclusive economic zone: 200 nautical miles
The length of the coasts is 1,527.28 kilometers, without including the country’s five adjacent islands and a large quantity of cays and small islands whose coastal length is 139 kilometers. The Dominican Republic has maritime territory in 16 provinces and the National District.
Border Lines
The border with the Republic of Haiti is conventional (established by equal negotiations between the bordering States). The border line measures 382.8 kilometers in length and extends from the mouth of the Dajabón river (also named Masacre), in the northeast of the island, to the mouth of the Pedernales river, in the southeast.
The border was established on June 3, 1777, when the Treaty of Aranjuez was signed in the Spanish city of the same name.


